The Descent
of the English language

The
history of English has been distinguished and denied into three different
periods, The period from the arrival of the English in Britain, down to
about 1100 is usually called the old
English or the Anglo-Saxon period. Following the earliest age, the period from
1100 to 1500 is called the middle English and from 1500 to the present day is
called modern English, although migration of the English people from the
continent of Europe had started during the 5th and the 6th centuries very few
records of English writing is available before 700.
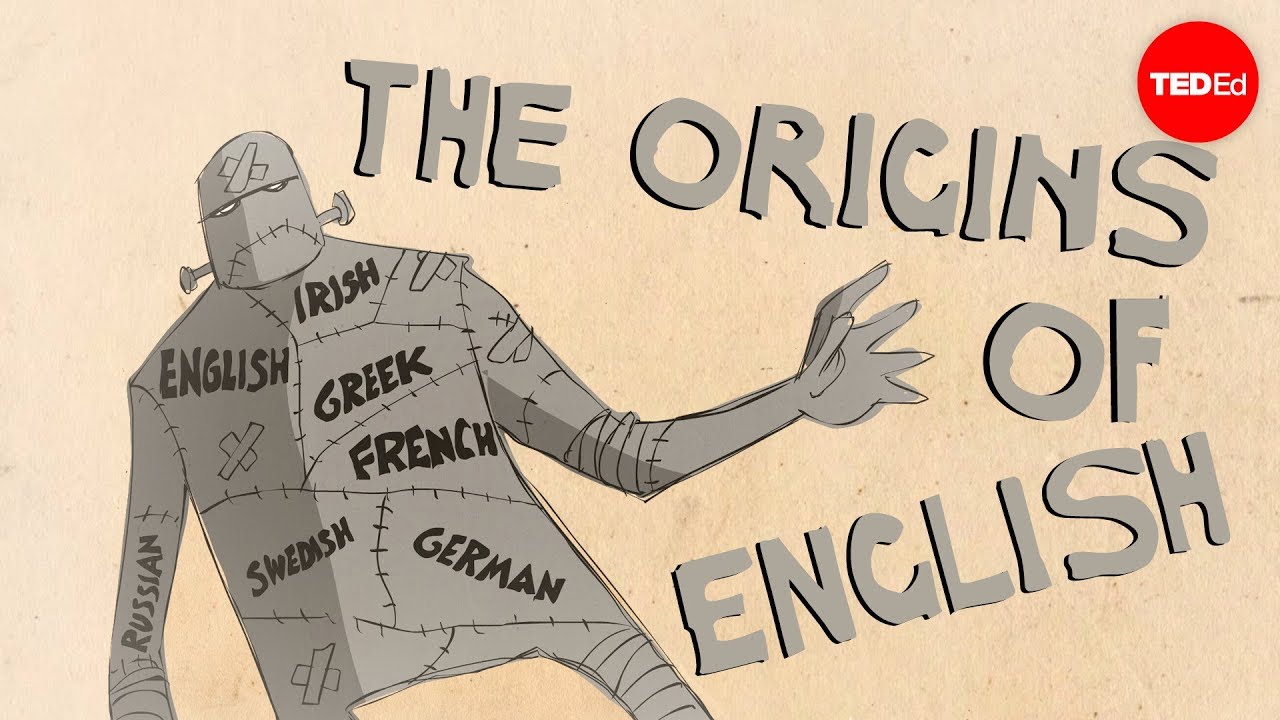
Indo-European family of language:
Our
English vocabulary is not to be studied in isolation, but it is related in one
way or the other to many languages of the world, the proper beginning therefore
is to views the place of English by taking into accountable many other tongues
of mankind.
For
example, the people who know German language might have noticed a remarkable
similarity between English and German, for instance, the German word “Milch” is
very close in sound to the English ‘Milk’, likewise, the German “Wasser” is
closer to the word “water” there are many other similarities between different
words of German, Dutch, Spanish and English.
The
English language has had a remarkable history, and when we take a sight of
historical records of English as a language, we can say that, it is a language,
in particular speech of some not to civilized tribe on the continent of Europe
along the north sea, of course, it had a still earlier history, going back
perhaps to somewhere, in eastern Europe or Western Asia. The most remarkable
thing about English language is that how it changed from being the speech of a
few small tribes to becoming the major language spoken on earth.
Considering
language in isolation, we can say that it is a system of conventional vocal
signs by mean of which human beings communicate, language includes the aspects
of signs, vocals, conventional speech patterns, and communication.
As we
discussed earlier English, German, Dutch, and Danish are almost like in terms
of pronunciation on the basis of this we may conclude that the similarity among
these language are due to borrowing, because there languages are spoken by
people living relatively closer to one another but that is not the case.
If we
extent the similarity within languages to Spanish, French, Latin and Greek, we
can see that there are further questions that arises in so far as the
patterning of English is concern. The resemblance between all the eight
languages, is that they are the descents of a single parent language.
Thus, Most
of the major languages of Europe and some of the languages of Asia belong to
one family known as Indo - European family of languages.
The
original Indo-European parent language became dead long before written records
have existence, it was spoken by pre-historic people, whose homeland was
somewhere in eastern Europe, it was perhaps between 3000 to 2000 BC, and it was
during that time the people started migrating to other places, during the
centuries that followed the Indo-Europeans moved rest world, in Europe and
South countries in Persia and India, and it suppressed all the local languages.
It is
believed that the only language that has survived from the Pre-Indo-European
tongues of Europe is “Basque” (Language of Spain Local), but as we know the
language is constantly changing and as the various groups of Indo-Europeans
became isolated from one another in Europe as well as in Asia and the languages
began to evolve in their own way in various regions.
Eventually
a number of distinct came out and there was no longer one common tongue but a
series of completely different languages. Which further produced many more languages, from which some
languages died totally and other languages gave birth to the newer ones.
The modern
descendent of the common Indo-European parent may be deride into eight
principal group of branches...
1) Teutonic:
We should first of all consider the Teutonic branch as
it belongs to English, taking about the primitive Teutonic branch can be geographically devided into
three further languages, east north and west (three parts)
The east Teutonic languages did not survive in modern times,
their principal representative language was Gothic, which is to be found in the New Testament. The North Teutonic languages are spoken today, in the
Scandinavian countries like Denmark, Norway Sweden and Iceland. West Teutonic
is represented by German, Dutch and English.
2) Italic:
When Rome was only a small village, there were several
Italic languages having equal status with Latin, but as Rome achieved a
dominant position in the ancient world all these languages disappointed. The
modern descendent of Latin usually called roman languages, show by their
geographical distribution something of the extant of Roman Empire. In France
and Spain the Roman conquest resulted in the complete displacement of the
earlier languages by Latin.
3) Hellenic: (Greek
Culture)
The Hellenic branch of Indo European family is today represented by
modern Greek, which is the descendent of the classical Greek of Plato and
Aristotle, and the common Greek dialect of the eastern meditation area in which
the New Testament was written.
4) Celtic languages:
More than
2000 years ago, the Celtic languages were spoken throughout a wide area of
western Europe generally in France, Spain and Great Britain but through the
Roman conquest Latin replaced all the Celtic language, but still Celtic language
s exists in Ireland and Wales (Welsh, UK).
5) Deltoslavic :
The Slavic
languages are spoken in Russia, Poland, and Czechoslovakia. The Deltaic groups
do not matter as much It compresses mainly Latvian languages, which was absorb
by the soviet union 1940.
6) Indo-Iranian:
The oldest
literary work in any Indo European language is written in an Indian language
Sanskrit, as the earliest 1500 BC, many books were published in this language
Sanskrit has always been of great interest to all the linguistics. Another
language was Romany, it was the language was thy gypsy who roamed about in
Europe and America but their native was long ago in the north western part of
India.
7) Armenian:
Now, no
longer used, its modern Armenian version is spoken in Turkey and Russia.
8) Albanian:
The only
surviving representative of the Albanian which is spoken in North Greece.
Conclusion:
Because all of these languages have come from a common
ancestors they are called cognate language and the similarities between them
which are not only of vocabulary but also of grammar. We must remember however
that Indo-European is only one of a number of language families throughout the
world.
No comments:
Post a Comment